
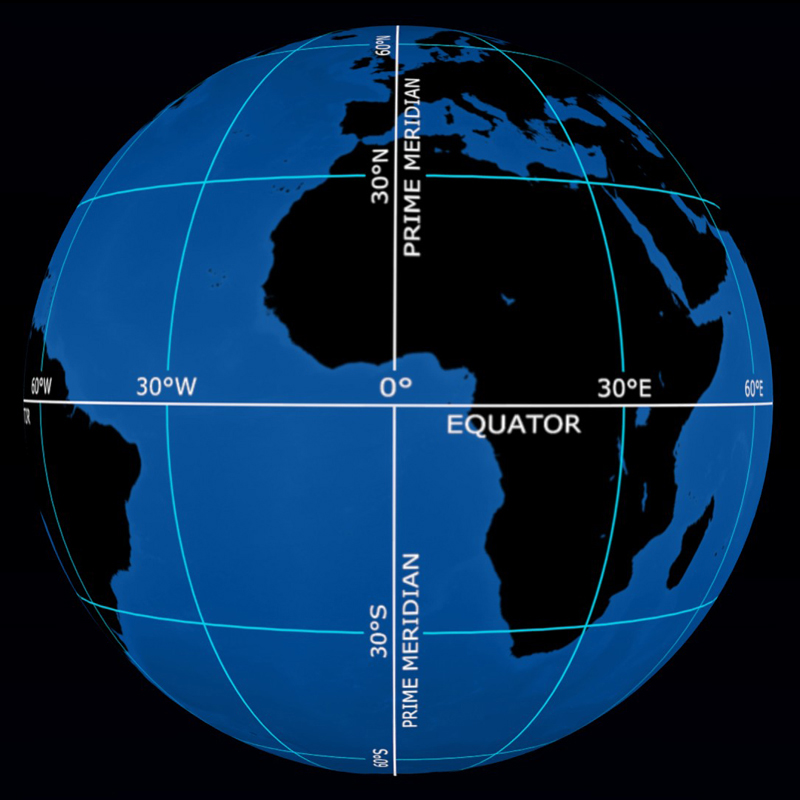
Again, the winter and summer seasons are switched. If you’re in an area with coordinates greater than 66.5 degrees latitude in either direction, you will experience 24-hour sunlight in the summer and 24-hour darkness in the winter. The Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle are located at 66.5 degrees north and south respectively. Summer in the southern hemisphere is from December to February. Remember, seasons are opposite depending on which side of the equator you’re on. These areas will experience the same super-high sun as areas in the Tropic of Cancer, but their summer is in December. The Tropics of Capricorn range from the equator to 23.5 degrees south. In the summer, which is in June, locations in the Tropic of Cancer will see the sun at the highest possible point in the sky: straight up. The Tropics of Cancer span from the equator to 23.5 degrees north. The tropics are considered any area within 23.5 degrees of the equator. While the prime meridian is the only notable longitude line, there are a few important latitude lines besides the equator.
Geographic and geocentric latitudes can differ by as much as 12 minutes of arc, an amount equivalent to a distance of more than 30 km on the ground.Other Notable Guidelines Credit: seefromthesky/ Unsplash On the WGS84 ellipsoid, the length of a degree of latitude increases from 110.574 km at the equator to 111.694 km at the poles. Whenever the unqualified term latitude is used, it will normally mean the geographic latitude. Unlike geocentric latitude, this line does not typically pass through the centre of the ellipsoid. Geodetic or geographic latitude – which is what is normally measured – is the angle between the plane of the Equator and the line, which is normal to the ellipsoid at the point of interest. Geocentric latitude is measured from the centre of the ellipsoid. As a result there is more than one way in which latitude is commonly measured. The distance is about 111 km at the Equator, reducing to 0 km at the Poles.Īlthough it is often convenient to think of the Earth as being spherical, in reality, its shape approximates more closely to that of an ellipsoid – a sphere that is flattened towards the poles. Each degree of longitude however, corresponds to a distance that varies with latitude. Each degree of latitude corresponds to a distance on the Earth‘s surface of about 111 km. Geographers and cartographers trace imaginary horizontal and vertical lines across Earth’s surface to locate points on the globe. Each degree (°) is subdivided into 60 minutes (') and each minute into 60 seconds ("). The main difference between Equator and Prime Meridian is that Equator is the line circling the Earth halfway between the North and South poles while Prime Meridian is the line that runs through Greenwich, England. Latitude and longitude are both measured in degrees. In 1884, an international conference decided that the Greenwich Meridian, as defined by the Airy Transit Circle at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, should be adopted as the Prime or Zero Meridian for the World.

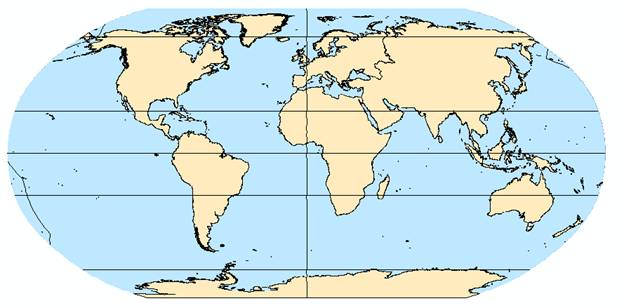
The north–south line passing through any particular point on the Earth’s surface is known as the “local meridian”.Īlthough the Equator is the obvious zero point from which to measure latitude, there is no equivalent point from which to measure longitude. Whilst lines (or parallels) of latitude all run parallel to the Equator, lines (or meridians) of longitude all converge at the Earth’s North and South Poles. Latitude is a measure of how far north or south somewhere is from the Equator longitude is a measure of how far east or west it is from the Prime Meridian.

Lines of latitude and longitude form the grid system used on globes, maps and charts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
